EV Charging in the UAE: What Drivers Need to Know About DC vs AC
As electric vehicles become a common sight on UAE roads, one of the biggest questions drivers face is: how should I charge my EV? The answer depends on understanding the difference between DC fast charging and AC charging — and knowing when to use each.
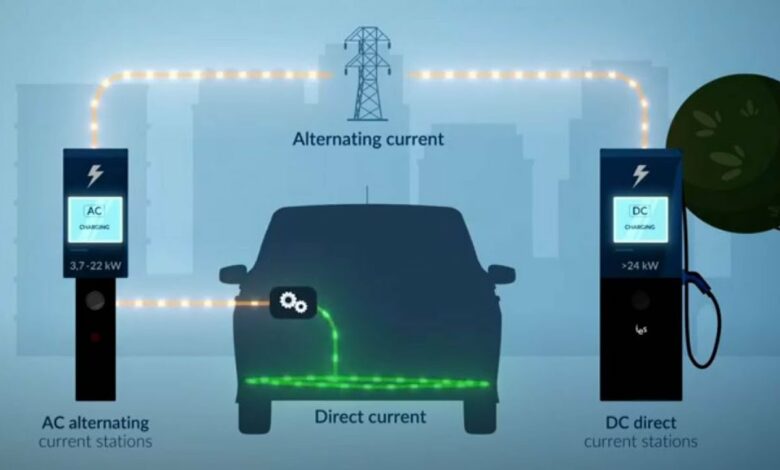
AC Charging (Home & Public Slow Chargers):
Most EVs come with onboard AC chargers, typically ranging between 7–22 kW. At this rate, a full charge can take several hours — ideal for overnight top-ups at home or while parked during work hours. AC charging is gentler on batteries, which means less long-term degradation. For most daily commutes within Dubai or Sharjah, AC charging is perfectly sufficient.
DC Fast Charging (Public High-Power Stations):
DC chargers deliver high power directly to the battery, skipping the car’s onboard converter. In the UAE, many public stations now offer 50–350 kW, allowing a 10–80% charge in 20–40 minutes. This is ideal for road trips between cities, emergency top-ups, or long days with heavy driving. However, frequent use of DC fast charging generates more heat and may slightly impact long-term battery health.
Connector Types:
The UAE’s infrastructure supports multiple standards, with CCS2 emerging as the most common for European and American EVs, CHAdeMO for some Japanese models, and Type 2 AC widely available. Always check your car’s compatibility when planning routes.
Practical Tips for UAE Drivers:
-
Use AC charging as your main solution, especially for daily commuting.
-
Reserve DC fast charging for inter-emirate journeys or quick recovery when needed.
-
In summer, pre-condition the cabin while plugged in — this preserves driving range and keeps batteries within optimal temperature.
Conclusion:
The UAE’s charging network is expanding rapidly, and with the right mix of AC and DC use, drivers can enjoy maximum convenience without compromising battery life. The key is knowing which charger to use, when, and why.







